



HP-STAP is an airborne noise testing and analysis software designed for sound pressure level (SPL) analysis and sound intensity level analysis. It provides clear time-domain waveforms, frequency-domain SPL results, and supports A / C / Z frequency weighting selection for practical acoustic measurement workflows
| SPL calculation clarity | Converts measured sound pressure (Pa) into SPL (dB) using the standard logarithmic definition. |
|---|---|
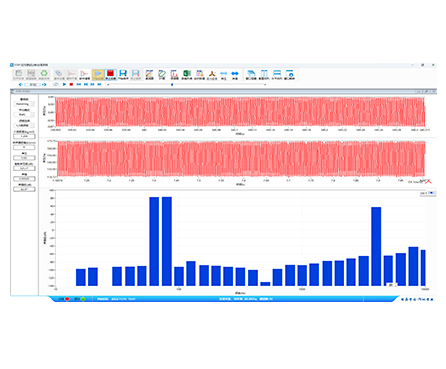
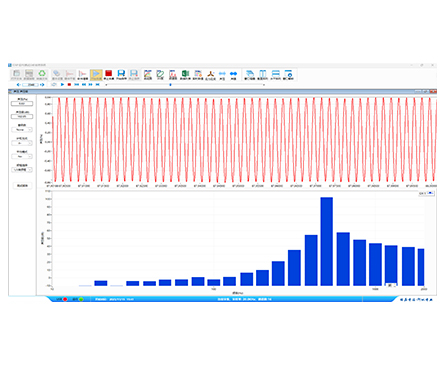
| Time waveform view | Quickly validate signal quality with pressure vs time display. |
| Frequency result view | Identify dominant noise bands with SPL vs frequency display. |
| Weighting flexibility | Choose A / C / Z weighting to match measurement and calibration needs. |
| Sound intensity insight | Analyze two-channel intensity probe data to obtain intensity level and frequency distribution. |
Product line: HP-STAP Series
Product type: Airborne Noise Testing & Analysis Software
Core capabilities:
Sound Pressure Level (SPL) analysis
Sound Intensity Level analysis (dual-microphone intensity probe)
Time-domain waveform visualization (pressure vs time)
Frequency-domain results visualization (SPL vs frequency)
A / C / Z frequency weighting selection
HP-STAP helps engineers quantify airborne noise using standard acoustic metrics:
Sound pressure (p): RMS value of instantaneous sound pressure over a time period
Sound pressure level (Lp):
Lp=20log10(p/p0)L_p = 20 \log_{10}(p / p_0)Lp=20log10(p/p0)
Where:
Lp: sound pressure level, dB
p: sound pressure, Pa
p₀: reference sound pressure, 20 μPa
For sound intensity work, HP-STAP processes two-channel signals captured by a dual-microphone sound intensity probe to compute sound intensity level and its frequency distribution.
Airborne noise testing in labs and production environments
Product noise evaluation (fans, motors, appliances, electronics, machinery enclosures)
Engineering troubleshooting: finding dominant frequency bands and noise patterns
Acoustic measurement tasks requiring A-weighted SPL reporting
Sound intensity measurements using dual-microphone intensity probes
Microphone / acoustic measurement instrument input for sound pressure signals
Dual-channel input for sound intensity analysis using a dual-microphone sound intensity probe
Frequency weighting support:
A-weighting (commonly used for representing human hearing characteristics)
C-weighting
Z-weighting (zero/flat weighting)
Calibration weighting guidance (by calibrator frequency):
1 kHz calibrator output: A / C / Z weighting can be selected (all are 0 dB at 1 kHz)
500 Hz or 250 Hz calibrator output: use C or Z weighting
125 Hz calibrator output: use Z weighting
SPL metric: Sound Pressure Level (Lp), unit dB
Sound pressure: RMS sound pressure, unit Pa
Reference sound pressure: p₀ = 20 μPa
Formula: Lp=20log10(p/p0)L_p = 20 \log_{10}(p / p_0)Lp=20log10(p/p0)
Displays / Outputs:
Time-domain waveform: X = time, Y = sound pressure
Frequency-domain SPL result: X = frequency, Y = SPL
Weighting options: A / C / Z frequency weighting
Sound intensity level analysis: two-channel computation + frequency distribution output
1) What is sound pressure (p) in HP-STAP?
It is the RMS value of instantaneous sound pressure over a period of time (unit: Pa).
2) How does HP-STAP calculate SPL (Lp)?
It uses the standard definition: Lp = 20·log10(p/p₀), where p₀ = 20 μPa, and Lp is in dB.
3) What’s the difference between sound pressure level and sound intensity level?
SPL: derived from sound pressure (single-channel pressure measurement).
Sound intensity level: computed from two-channel signals captured by a dual-microphone intensity probe, giving intensity level and its frequency distribution.
4) Which weighting should I use during calibration?
1 kHz: A / C / Z all acceptable
500 Hz or 250 Hz: use C or Z
125 Hz: use Z
5) Why is A-weighted SPL widely used?
Because A-weighting better represents human hearing characteristics, it’s widely applied in noise measurement practice.